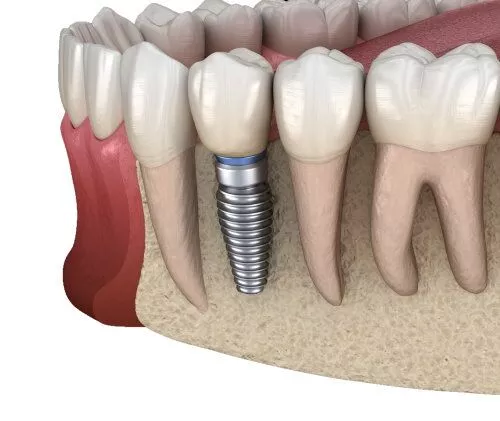
A dental implant is a surgical component that is placed in the jawbone to serve as an artificial tooth root. It provides a strong foundation for a replacement tooth or a bridge, and it can be a long-lasting solution for individuals with missing teeth. Here’s a detailed explanation of dental implants:
Components of a Dental Implant:
- Implant Fixture: This is the part that is surgically implanted into the jawbone. It is typically made of biocompatible materials such as titanium. The implant fixture resembles a small screw or post and serves as an artificial tooth root.
- Abutment: The abutment is a connector piece that attaches to the implant fixture and protrudes above the gum line. It acts as a support for the replacement tooth or crown.
- Crown or Prosthesis: The crown is the visible part of the dental implant. It is custom-made to match the color, shape, and size of your natural teeth, ensuring a natural appearance. The crown is typically made from materials like porcelain or ceramic.
The Dental Implant Procedure:
The dental implant process is typically performed in multiple stages and may span several months. Here are the key steps involved:
1. Initial Consultation:
- During your first visit, your dentist or oral surgeon will conduct a thorough examination, which may include X-rays or CT scans to assess the condition of your jawbone and determine if you are a suitable candidate for dental implants.
2. Implant Placement:
- If you are deemed a candidate, the implant fixture is surgically placed into your jawbone. This is done under local anesthesia or sedation to ensure you are comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
- Over the next few months, the implant fixture undergoes a process called osseointegration, during which it fuses with the surrounding bone tissue. This fusion provides a stable and strong foundation for the replacement tooth.
3. Abutment Placement:
- Once osseointegration is complete (which can take several months), a second minor surgical procedure may be required to attach the abutment to the implant fixture.
- The gum tissue is then allowed to heal around the abutment for a few weeks.
4. Crown Placement:
- After the gums have healed and the abutment is firmly in place, an impression is taken of the abutment and the surrounding teeth.
- A custom-made crown is created in a dental laboratory to perfectly match your natural teeth.
- The crown is then attached to the abutment, completing the dental implant restoration.

Benefits of Dental Implants:
- Improved Aesthetics: Dental implants look and feel like natural teeth, providing a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
- Functionality: Implants restore the ability to chew and speak comfortably, often better than other tooth replacement options.
- Durability: When properly cared for, dental implants can last a lifetime, making them a long-term solution for tooth loss.
- Preservation of Jawbone: Implants stimulate the jawbone, preventing bone loss and maintaining facial structure.
- No Impact on Adjacent Teeth: Unlike traditional bridges, dental implants do not require the alteration of neighboring healthy teeth.
- Enhanced Confidence: Dental implants can boost self-esteem and confidence by restoring a complete and natural-looking smile.